What Is the Quasimodo (QM) Pattern in Forex?
The Quasimodo pattern (QM) is a valuable tool for Forex traders, helping identify early entry points as new trends emerge following a market reversal.
Essentially, the QM is a reversal pattern that signals the start of a new trend after the market reaches a significant high or low. Its structure allows traders to place stop-loss orders precisely and track trend movements more accurately.
Pattern Structure and Key Components
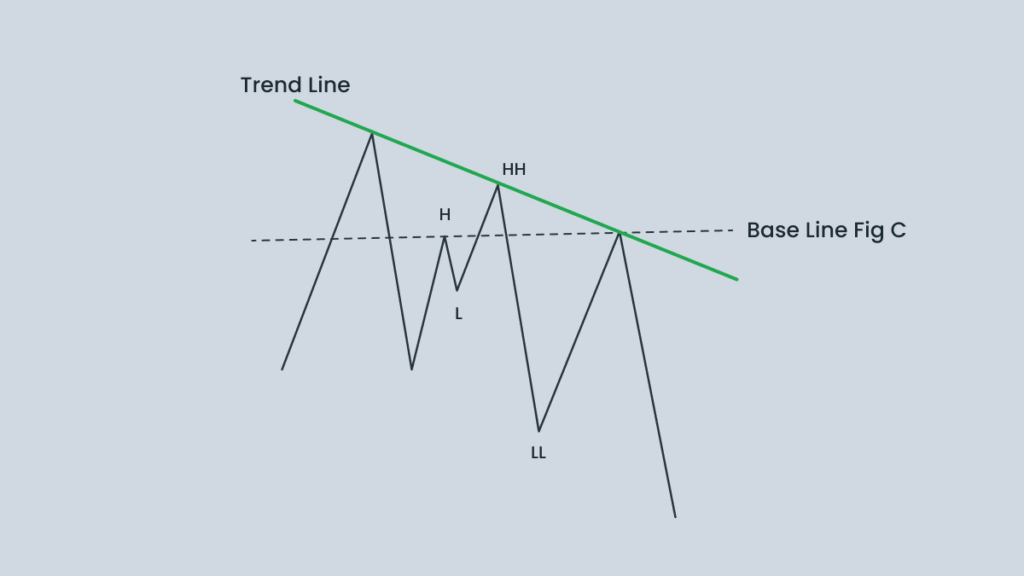
How can you spot a Quasimodo pattern on a chart? The pattern typically features three distinct peaks or troughs, depending on whether the scenario is bearish or bullish. Its name comes from Victor Hugo’s character, reflecting the asymmetric shape of price movements.
The Quasimodo pattern forms under five key conditions:
- A strong bullish or bearish trend creates a higher high or lower low.
- A false breakout occurs, initially appearing as if the level has been breached, followed by a pullback.
- A sharp reversal confirms the breakout failure.
- The original zone is retested, often at the point where the breakout failed.
- An entry signal forms when price re-enters the base zone.
Types of Quasimodo Patterns
- Bearish Quasimodo: The middle peak is the highest, flanked by slightly lower peaks on either side. This formation indicates a potential downtrend.
- Bullish Quasimodo: The middle trough is the lowest, with slightly higher peaks on either side. This signals a possible reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.

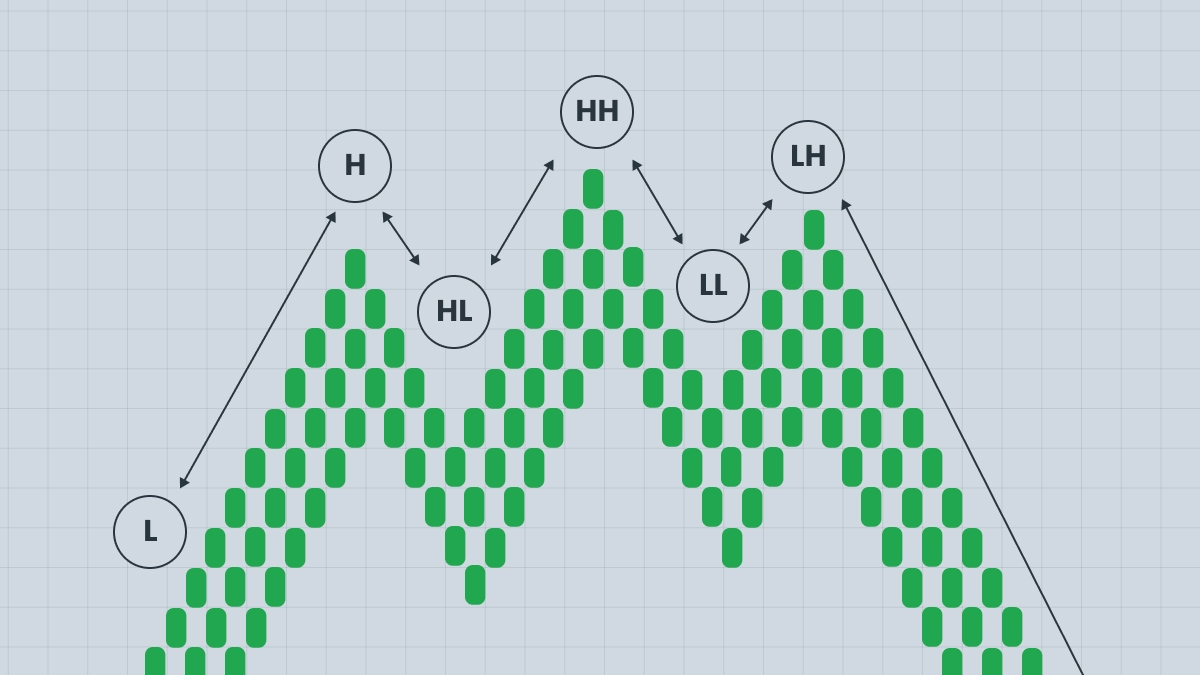
Quasimodo Structure and Key Terms (QML + HH/LL Sequence)
What does the pattern really represent?
While the Quasimodo pattern may seem complex at first, the concept is straightforward:
The market moves in one direction, fakes a breakout, then reverses sharply. The ideal entry point is when price returns to retest the previous level, known as the Quasimodo level (QML).
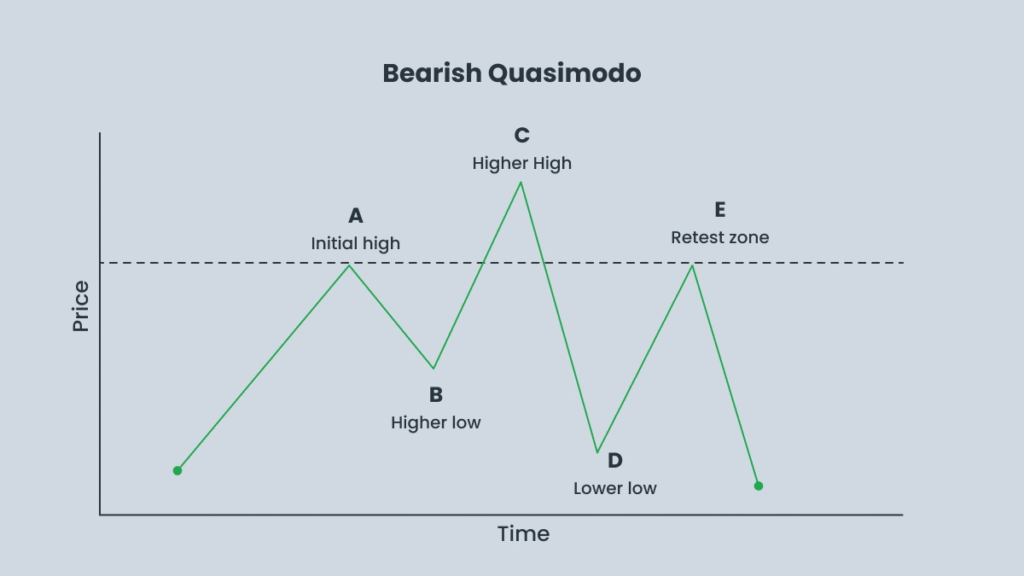
Bearish Quasimodo Example:
- Price forms a higher high, giving buyers the impression that the uptrend will continue.
- The market suddenly reverses, creating a lower low and breaking the uptrend.
- Price then retraces to the previous high (the left shoulder / QML) and begins to stall. This is the signal to enter a sell position.
If price rises above the head (the highest high), the pattern is invalid, and the trade setup should be ignored.
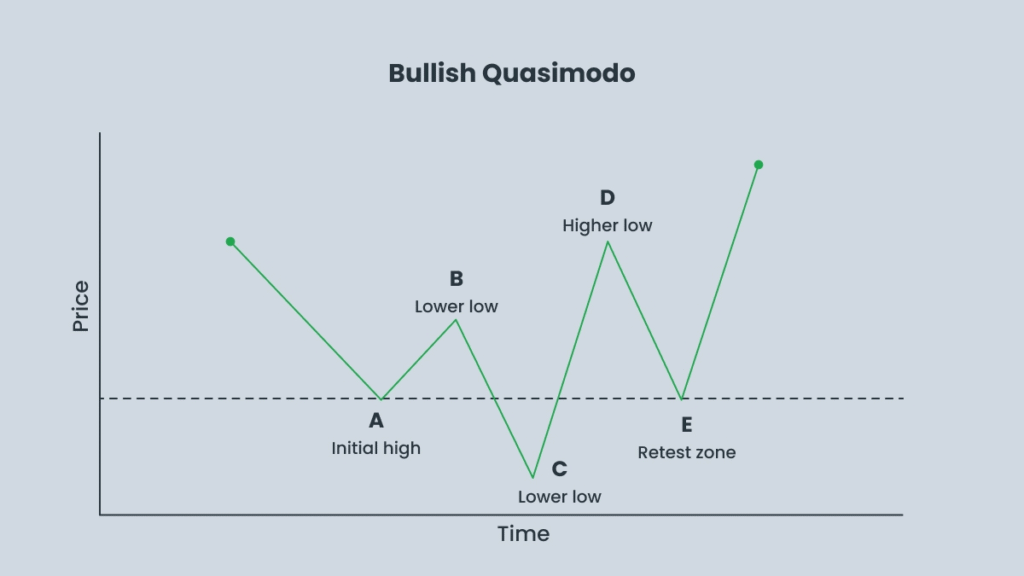
Bullish Quasimodo:
- Price forms a lower low, making sellers believe the downtrend will continue.
- The market then reverses sharply, creating a higher high and breaking the downtrend.
- Price retraces to the previous low (the left shoulder / QML) and begins to stall. This is the signal to enter a buy position.
If price falls below the head (the lowest low), the setup becomes invalid, and the trade should be avoided.
Get high-accuracy trading signals delivered directly to your Telegram. Subscribe to specialized packages tailored for the world’s top markets:
Free Crypto Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free Forex Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free VIP Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices) Subscribe via Telegram
Free Trading Acoount Open With ORON LIMITED Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices)
Open Account
Not profitable? Don’t worry! Join our copy trading system where we provide lower risk returns. Benefits of Joining Us:
-Lesser Risk as lot size is minimal
-Higher returns (approx. 5% to 10% monthly)
-Easy Deposit and Withdrawal with USDT using crypto wallets
-Lesser Drawdown
-Instant Support
-Invest Now and get guaranteed returns with us. DM us for more info❤️
-Start Now
*Copy Trading is free but we charge some percentage of profit as fees.*
Full VIP signals performance report for September 22–26, 2025:
Quick Identification Checklist:
- Identify a clear uptrend or downtrend.
- Look for the “trap” move — a new extreme high or low that quickly fails.
- Wait for price to break the previous structure in the opposite direction.
- Enter the trade when price retests the Quasimodo level (QML).
- Always use a stop-loss beyond the head to manage risk.
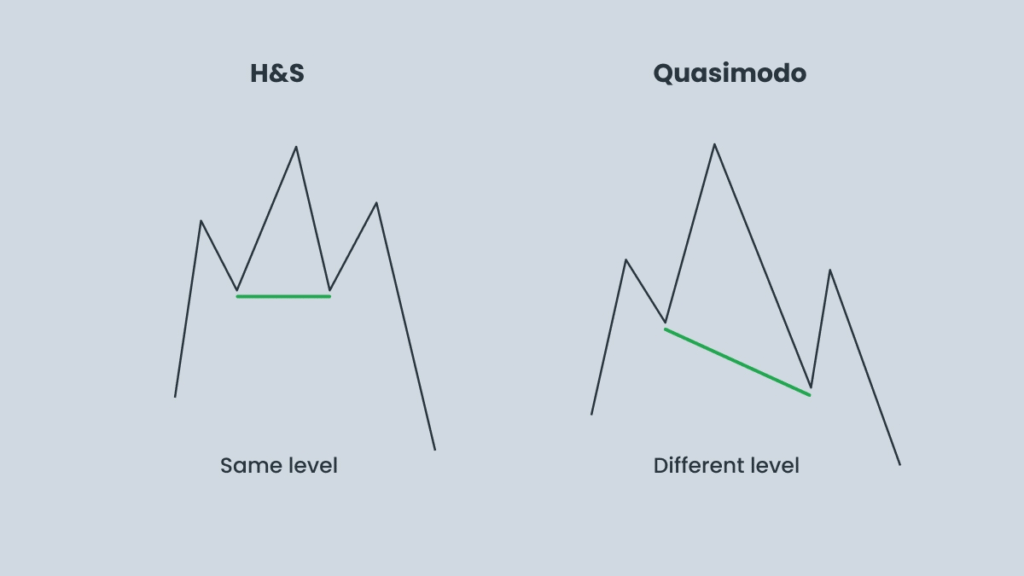
Quasimodo vs. Head and Shoulders: Key Differences
The Quasimodo (QM) pattern can sometimes be confused with the Head and Shoulders (H&S) pattern. While both are reversal patterns featuring three peaks or troughs and a central “head,” they differ in structure, entry points, and mechanics.
Pattern Structure:
- Head and Shoulders:
- Bearish: three highs and two lows, with the middle peak being the highest.
- Bullish: three lows and two highs, with the middle low being the lowest.
- Confirmation occurs when price breaks the neckline, signaling a likely reversal.
- Quasimodo:
- Based on higher highs and lower lows.
- The reversal is sharper and alters the prior trend’s structure.
- Unlike H&S, the price first breaks the previous structure and then retests the left shoulder (QML).
- If you draw a neckline, it is usually tilted, and the third extreme (minimum for bullish QM, maximum for bearish QM) exceeds previous levels before reversing.
This pattern strategy is often referred to as HHLL, and while it may appear under different names, it’s grounded in classic Forex principles. One advantage is that no indicators are required to use it effectively.
Entry Logic:
- Head and Shoulders: Enter when the right shoulder crosses the neckline. This offers a predictable target, often at least the height of the head.
- Quasimodo: Allows for an earlier entry, typically at the retest of the last structural level (point A), before the neckline. This can offer a better risk-to-reward ratio, but requires precision. The assumption is that price will bounce off the second peak, forming the pattern, and continue in the direction of the anticipated reversal.
Bearish vs. Bullish Variations of the Quasimodo Pattern
| Pattern Type | Structure | Trade Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Bearish Quasimodo | HH – LL – Retest | Sell setup |
| Bullish Quasimodo | LL – HH – Retest | Buy setup |
In both bullish and bearish cases, the pattern involves a breakout of the internal structure, followed by a return to the base level (retest).
1. Bullish Quasimodo Pattern
- Appears at the end of a downtrend and signals a potential upward reversal.
- The market forms lower lows (LL) and lower highs (LH), leading traders to believe the downtrend will continue.
- Suddenly, the price breaks the structure and forms a new higher high (HH).
- It then retraces back toward the previous low, creating a bullish reversal opportunity.
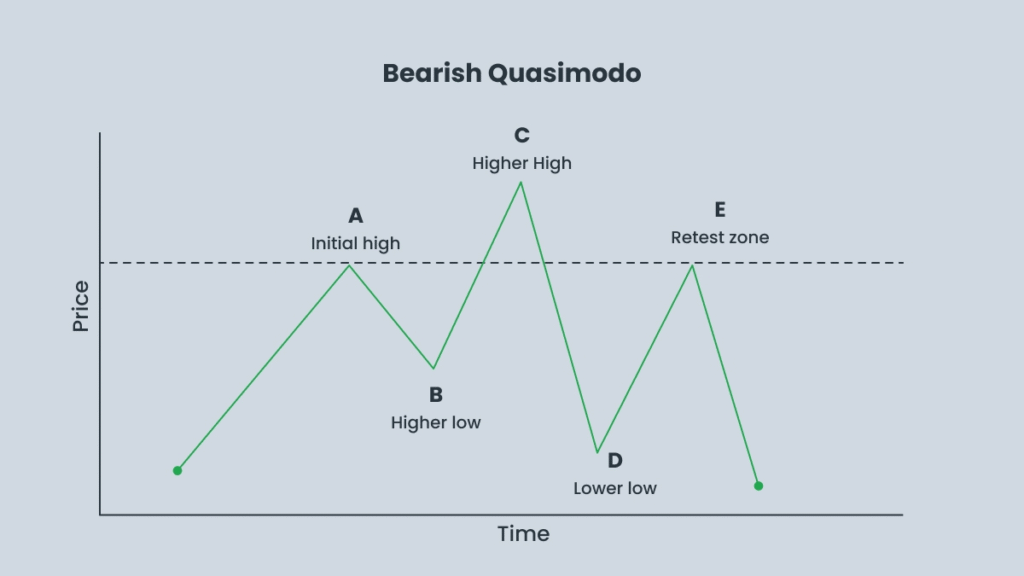
2. Bearish Quasimodo Pattern
- Occurs at the end of an uptrend and indicates a potential downward move.
- The market forms higher highs (HH) and higher lows (HL), trapping traders who enter on breakouts.
- The price breaks the structure, creating a new lower low (LL), and then retraces toward the previous high.
- This setup signals a potential sell opportunity.
Key Point:
Both bullish and bearish Quasimodo patterns require confirmation. Avoid rushing into a trade during the pullback; wait for a clear entry signal.
Practical Example of the Quasimodo Pattern in an Uptrend
- Point A – This marks the first sign of a potential reversal and future resistance. In a bearish Quasimodo setup, it represents the initial high of the uptrend.
- Point B – A corrective pullback occurs here, forming a temporary low that acts as the neckline of the pattern.
- Point C – The price moves higher than Point A, creating a new extreme. This is the highest peak in a bearish Quasimodo pattern and signals potential resistance ahead.
- Point D – The price reverses sharply, forming a lower low that breaks the neckline at Point B. This movement confirms the trend reversal is developing.
- Point E – The price retraces back toward Point A, which now acts as resistance without surpassing Point C. This represents an optimal entry point for a sell trade.
In a Downtrend: The same principles apply in reverse, where the pattern signals a potential bullish reversal.
I can also rewrite the downtrend version fully with Point labels for symmetry, so it’s easy to visualize both bullish and bearish Quasimodo patterns. Do you want me to do that?
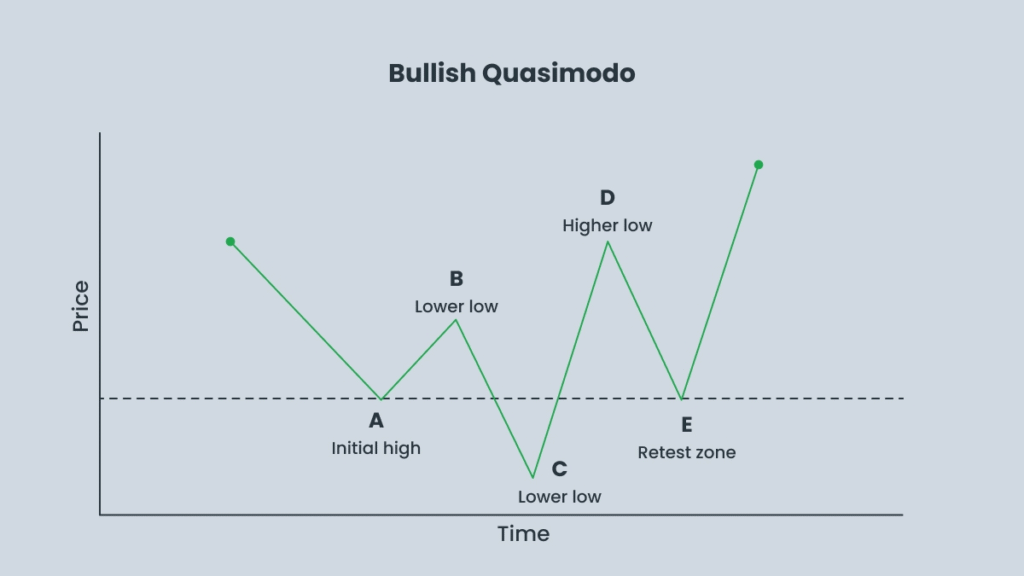
Example of the Quasimodo Pattern in a Downtrend
- Point A – Marks the start of the downtrend and forms the penultimate low, signaling a potential trend reversal.
- Point B – A corrective pullback occurs, creating a temporary high and establishing horizontal resistance.
- Point C – The price resumes its decline, forming a lower low. This level becomes future support and marks the end of the downward move.
- Point D – The market forms a higher high, known as the Quasimodo level (QML), confirming a potential bullish reversal.
- Point E – The price retraces back to the level of Point A, offering an optimal entry point for a buy trade.
Quasimodo Continuation Pattern
Not all Quasimodo patterns indicate the end of a trend. Sometimes the same structure forms within an existing trend, pushing in the current direction. This is called a Quasimodo Continuation.
Structure and Logic
In a bullish continuation:
- The market is already in an uptrend.
- Price dips to a temporary lower low (a shakeout), then breaks above the previous high (Break of Structure, BOS).
- It pulls back to retest the Quasimodo level (the left shoulder) before continuing upward.
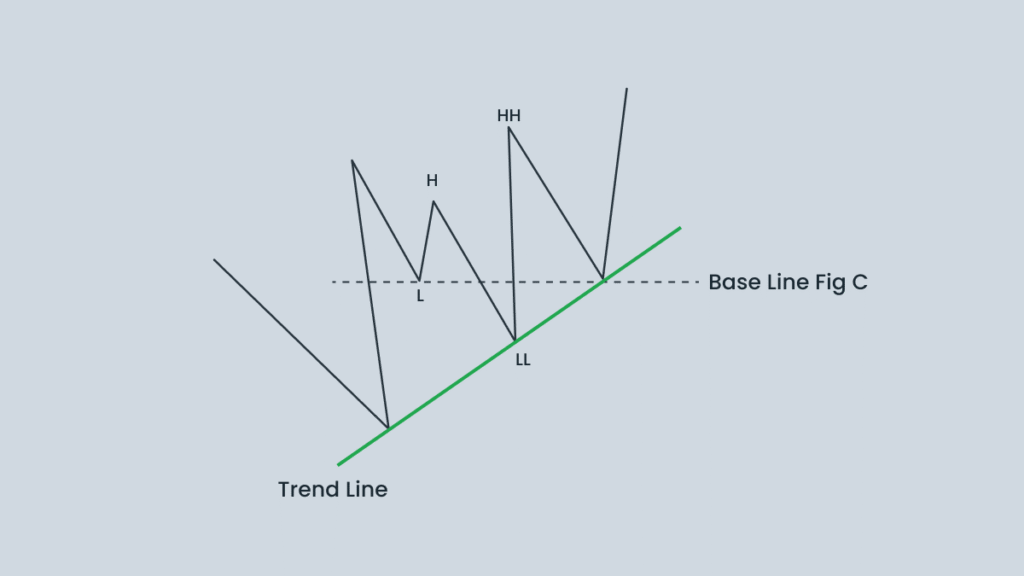
In a bearish continuation, the process is reversed. The price forms a temporary higher high, catching breakout buyers off guard. It then breaks below the previous low and eventually retraces to retest the left shoulder, providing a signal for a new short entry.
Get high-accuracy trading signals delivered directly to your Telegram. Subscribe to specialized packages tailored for the world’s top markets:
Free Crypto Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free Forex Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free VIP Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices) Subscribe via Telegram
Free Trading Acoount Open With ORON LIMITED Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices)
Open Account
Not profitable? Don’t worry! Join our copy trading system where we provide lower risk returns. Benefits of Joining Us:
-Lesser Risk as lot size is minimal
-Higher returns (approx. 5% to 10% monthly)
-Easy Deposit and Withdrawal with USDT using crypto wallets
-Lesser Drawdown
-Instant Support
-Invest Now and get guaranteed returns with us. DM us for more info❤️
-Start Now
*Copy Trading is free but we charge some percentage of profit as fees.*
Full VIP signals performance report for September 22–26, 2025:
Why the Quasimodo Pattern Works
The Quasimodo continuation traps traders who anticipate an early reversal. The false breakout, or “head,” triggers a surge of activity, while the Break of Structure (BOS) reaffirms the dominant trend. Smart money often uses the retest of the Quasimodo level (QML) to add positions in the direction of the prevailing trend.
Trading Rules
- Identify a clear dominant trend (H4/D1 charts provide the clearest signals).
- Spot the false breakout against the trend (the “head”).
- Wait for the BOS that aligns with the dominant trend.
- Enter when the price retests the left shoulder (QML) with confirmation.
- Place stops beyond the head and set profit targets in line with the prevailing trend.
Indicator Setup: Tools to Identify a Quasimodo Pattern
Traders rely on several tools to spot Quasimodo patterns effectively:
- Trendlines and Fractals: Essential for marking swing highs and lows, since QMs form only within a clear trend.
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): Regular divergence can indicate an upcoming reversal, while hidden divergence may signal trend continuation.
- Price Rectangles: Sideways movement between support and resistance can form part of the QM, where failed swings precede the reversal.
- RSI & MACD: Divergence between price and momentum suggests weakening strength and potential reversal points.
- Moving Averages: Crossovers (e.g., 20 EMA crossing 50 EMA) can confirm shifts in market direction.
- Volume: Increased volume during a BOS or QML retest often indicates participation by major players, strengthening the setup.
- Fibonacci Levels: When the Quasimodo level aligns with key ratios (e.g., 61.8% or 78.6%), the probability of a successful reversal rises.
Spotting and Trading a Quasimodo
- Confirm a clear trend exists before the QM forms.
- Zoom out to filter out minor pullbacks and note significant structure breaks.
- Identify the minimum or maximum followed by a corrective pullback.
- Wait for the price to retest the original zone.
- Look for confirmation signals, such as RSI divergence.
No single indicator guarantees a QM pattern; the best approach combines logic, patience, and supporting tools like trendlines and imbalances.
Checklist for Trading Quasimodos
- Identify: Clear trend, false breakout, BOS.
- Confirm: Rejection or divergence at the Quasimodo level.
- Enter: On retest of QML with a confirmation candle.
- Stop-Loss: Beyond the head.
- Take Profit: Minimum 1:2 risk-to-reward.
- Trade Management: Move stop to breakeven at 1R and trail afterward.
Optimal Conditions for Quasimodo Patterns
Not all QMs are equally reliable. Their effectiveness depends on timeframe, market context, and volatility.
Timeframes:
- H4/Daily: Most reliable. Patterns take time to form and higher timeframes filter noise. Professional traders often focus here.
- M15–H1: Usable but riskier. Require extra confirmation due to frequent fakeouts.
Market Context:
- Supply & Demand Zones: Bullish QMs at demand zones or bearish QMs at supply zones are stronger signals.
- Trend Strength: Best setups follow strong trend extensions. Weak or sideways markets create unreliable patterns.
- Volatility: Moderate volatility is ideal—enough to break structure but not so extreme that the price jumps erratically. Major news events can invalidate the setup.
Practical Filters Before Trading a QM:
- What timeframe am I trading? Below H1 requires additional confirmation.
- Is the pattern forming inside a supply or demand zone? If not, skip it.
- Was the preceding trend strong? Weak trends produce less reliable patterns.

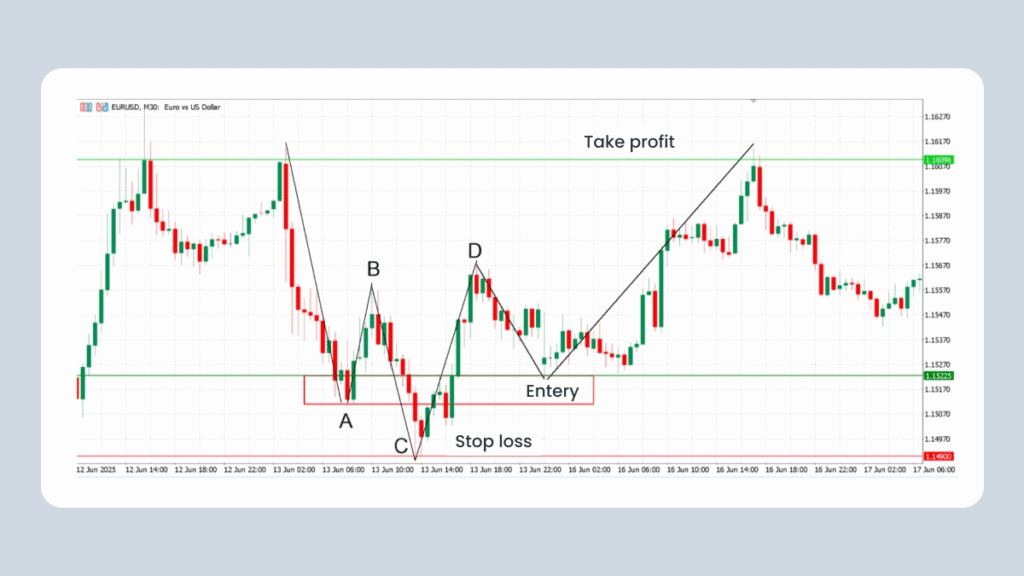
Entry Strategy: Buy and Sell Setups Explained
The entry approach depends on whether the Quasimodo pattern is bullish or bearish. Here’s a breakdown for a bullish Quasimodo:
- Identify the Quasimodo pattern by noting the key swing points: A, B, C, and D.
- Enter a long position at point A when the price retests the demand zone and pulls back from point D.
- Place a stop-loss just below the low of point C to control risk.
- Set your take-profit near the peak between the head and the right shoulder, aiming for a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2.
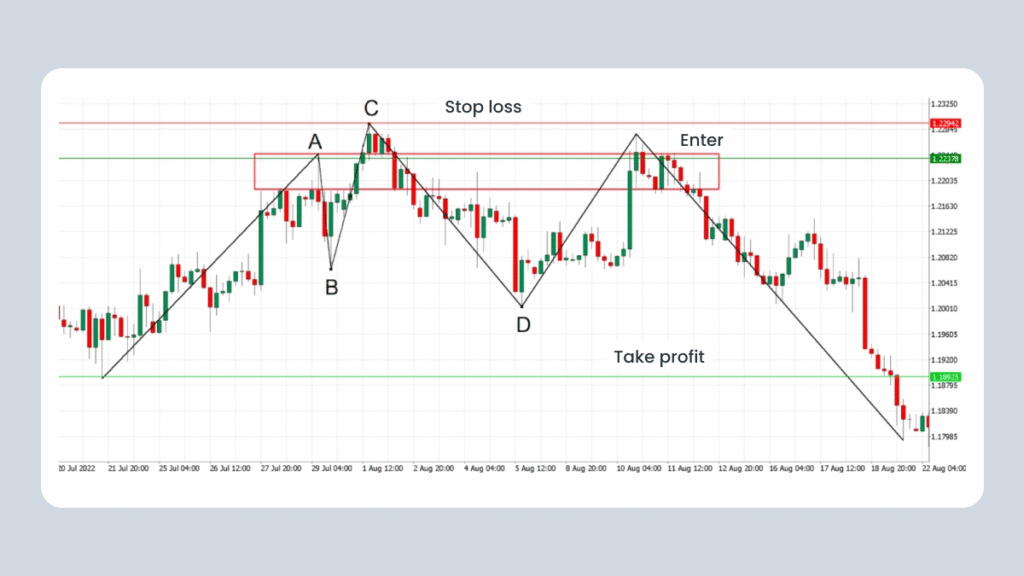
Steps for Trading a Bearish Quasimodo
- Identify the key swing points A, B, C, and D to outline the Quasimodo reversal pattern, just as you would for a bullish setup.
- Enter a short position near point A when the price retests its supply zone and retraces after point D.
- Place a stop-loss slightly above the high of point C to manage risk.
- Set your take-profit at previous support levels or target a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2 or higher.
Trade Management
Properly managing your trade is just as important as identifying the Quasimodo pattern. After entering, focus on protecting your capital while giving the setup room to develop.
ATR-based Stop Buffer
Instead of placing your stop-loss directly below (or above) the head, add a small cushion using roughly 0.5–1 times the ATR. This prevents normal market fluctuations from triggering your stop prematurely.
Risk per Trade
Keep your risk limited, ideally 1–2% of your account balance per trade.
Scaling Out
When the price moves roughly twice your risk (2R) in your favor, consider taking partial profits. For instance, close half your position and move your stop to breakeven. This locks in gains while allowing the remaining position to continue growing.
Trailing the Stop
As the trend progresses, adjust your stop accordingly. For a bullish QM, trail it below each new higher low; for a bearish QM, trail it above each new lower high. This secures profits without prematurely closing the trade.
Rechecking the Setup
Monitor market conditions continuously. If volatility spikes or structure shifts, reassess your stop and profit targets (1:2, 1:3, or higher if conditions allow). Quasimodo setups rarely form perfectly, so small adjustments help keep your trade aligned with the market.
Non-Standard Setups: Imperfect Quasimodos
Markets rarely produce textbook Quasimodos. The left shoulder might be messy, the head may extend too far, or the retest could be shallow. Adapting to these imperfections is key.
Common Imperfections and Adjustments
- Oversized Head: Point C may extend further than expected. Solution: Widen your stop and reduce position size. Skip the trade if the R:R falls below 1:2.
- Shallow Retest: Price may barely touch the Quasimodo level (A). Solution: Place a limit slightly before the level or wait for a clear rejection candle.
- Double Retest: Price might retest point A multiple times. Solution: Trade only the first retest at full size; subsequent retests are less reliable.
- Broken Symmetry: Swings from A to E may appear uneven or choppy. Solution: Zoom out. If the overall pattern still shows extension → BOS → retest, the setup can remain valid.

Advanced Position Management
While your entry rules define stop placement (just beyond point C) and aim for a 1:2 risk/reward ratio, real trading rarely unfolds like a textbook example. Here are some practical tips to manage positions more effectively:
- Add a cushion: Don’t place your stop exactly at point C—give it a few extra pips to account for spreads and intraday volatility.
- Scale out: Take partial profits at 2R and let the remaining position aim for a larger target.
- Trail your stop: In a bullish QM, move the stop below each higher low; in a bearish QM, above each lower high. This secures profits without closing the trade prematurely.
- Watch correlations: Avoid taking multiple QMs on highly correlated pairs. If one stops out, the others might follow.
Pros and Cons of the Quasimodo Pattern
Before trading Quasimodo setups live, consider both the advantages and limitations:
Pros:
- Allows early entries
- Clear structural formation
- Strong risk/reward potential
- Applicable across markets
- Flexible for various trading styles
Cons:
- Can be difficult to spot; takes practice
- False signals are common
- Requires confirmation
- Demands patience
- Highly context-dependent
Risks and Limitations
The Quasimodo pattern is powerful but not foolproof. Most failures come from ignoring its boundaries:
- Look-alikes: Many price swings resemble a Quasimodo until you zoom out. Without a clear higher high or lower low and a break of structure, the setup is invalid.
- Late identification: Waiting too long can mean missing the ideal entry point, leading to chasing the trade.
- Retest trap: Not every return to the QML provides a clean entry; price may cut through the level and trigger your stop.
- Market conditions: The pattern works best in trending markets. In choppy or sideways conditions, QMLs lose reliability.
- Discipline and pressure: Patience is key. Early or impulsive entries turn a structured setup into a gamble.
The Quasimodo pattern only works within proper context. Use it in trending markets, seek confirmation, and manage risk carefully with stops and targets.
Common Mistakes and How to Fix Them
- Ignoring confirmation signals
- Mistake: Entering immediately at the QML without waiting for rejection.
- Solution: Look for at least one confirmation, such as a rejection wick, RSI/MACD divergence, or a lower-timeframe structure break.
- Seeing QMs everywhere
- Mistake: Labeling any higher high or lower low as a Quasimodo.
- Solution: A valid QM requires a trend extension (point C) and a decisive BOS (point D) before retesting point A. No BOS, no trade.
- Entering before the pattern is complete
- Mistake: Entering at point D, before the retest at QML.
- Solution: Wait patiently for the price to return to point A (left shoulder level).
- Ignoring market context
- Mistake: Trading a QM against the higher-timeframe trend or outside key supply/demand zones.
- Solution: Filter setups by market structure and zones. Focus on H4/D1 charts for better reliability.
- Poor position sizing
- Mistake: Risking too much on a single trade because the setup “looks perfect.”
- Solution: Limit risk to 1–2% of your account per trade and ensure proper R:R before entry.
Get high-accuracy trading signals delivered directly to your Telegram. Subscribe to specialized packages tailored for the world’s top markets:
Free Crypto Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free Forex Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free VIP Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices) Subscribe via Telegram
Free Trading Acoount Open With ORON LIMITED Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices)
Open Account
Not profitable? Don’t worry! Join our copy trading system where we provide lower risk returns. Benefits of Joining Us:
-Lesser Risk as lot size is minimal
-Higher returns (approx. 5% to 10% monthly)
-Easy Deposit and Withdrawal with USDT using crypto wallets
-Lesser Drawdown
-Instant Support
-Invest Now and get guaranteed returns with us. DM us for more info❤️
-Start Now
*Copy Trading is free but we charge some percentage of profit as fees.*
Full VIP signals performance report for September 22–26, 2025: