The Two Main Ways to Succeed in Trading
When it comes down to it, long-term trading profitability boils down to two mathematically grounded approaches:
1. High Win Rate
This approach focuses on achieving many small, consistent wins.
- Example: A scalper might win 70–80% of trades, even if each profit is modest.
- Risk: A single large loss can erase multiple small gains, making tight stop-losses essential.
2. High Payoff Ratio
Here, winning trades are significantly larger than losing trades.
- Example: A trend trader using a 1:3 risk–reward ratio can remain profitable even with only a 35% win rate.
- Risk: This requires patience and the ability to endure losing streaks while waiting for substantial winners.
Every trading strategy—whether trend-following, counter-trend, or stop-management—falls into one of these two categories. The key is selecting a style that aligns with your personality, available time, and risk tolerance.
The Two Approaches to Trading
1. Trading with the Trend
Although what goes up must eventually come down, trends tend to persist longer than reversals. They can last months or even years. For example, the US500 index has generally trended upward over the past century—though past performance does not guarantee future results.
Traders use numerous tools to assess trend strength and duration across different timeframes, including technical indicators, chart patterns, and other analytical instruments. Predicting reversals, on the other hand, is far less reliable.
To trade effectively with the trend: enter in the direction of the trend, hold your position until clear reversal signals appear, then exit. For beginners, this momentum-based approach is a practical way to gain experience, though no strategy guarantees success.
Trend-Following Playbook
- Identify the Trend:
Check if the price is forming higher highs and higher lows (uptrend) or lower highs and lower lows (downtrend). Moving averages can help; for instance, if the 50 EMA is above the 200 EMA, it confirms an uptrend. - Entry Signals:
Look for pullbacks to support, resistance, or moving averages. Candlestick patterns like bullish engulfing (in an uptrend) or bearish engulfing (in a downtrend) can improve entry timing. - Stop Placement:
Place stops beyond the most recent swing low in an uptrend or swing high in a downtrend. ATR-based volatility stops are another option. - Trade Management:
Take partial profits at key support or resistance levels. You can also trail stops behind swing points or moving averages to protect gains as the trend develops. - Exit Signals:
Close the trade if the trend structure breaks, such as when a higher low fails in an uptrend. Other signals include moving averages crossing against your position or ADX dropping below 20, indicating the trend may be weakening.
2. Trading Against the Trend
[The next section would continue from here…]

Imagine a currency pair that has been trending upward for several months. The likelihood of the uptrend continuing is higher than that of an immediate reversal. While a pullback is inevitable at some point, accurately predicting the timing is extremely challenging—even for an experienced trader.
Get high-accuracy trading signals delivered directly to your Telegram. Subscribe to specialized packages tailored for the world’s top markets:
Free Crypto Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free Forex Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free VIP Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices) Subscribe via Telegram
Free Trading Acoount Open With ORON LIMITED Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices)
Open Account
Not profitable? Don’t worry! Join our copy trading system where we provide lower risk returns. Benefits of Joining Us:
-Lesser Risk as lot size is minimal
-Higher returns (approx. 5% to 10% monthly)
-Easy Deposit and Withdrawal with USDT using crypto wallets
-Lesser Drawdown
-Instant Support
-Invest Now and get guaranteed returns with us. DM us for more info❤️
-Start Now
*Copy Trading is free but we charge some percentage of profit as fees.*
Full VIP signals performance report for September 22–26, 2025:
Most of the time, traders who give in to the urge to go against the trend end up empty-handed, missing out on genuine trading opportunities that were right within reach.
Mean Reversion Trading
Mean reversion offers a systematic approach to trading against the trend. The core idea is that when a price moves too far in one direction, it often returns toward its average.
How It Works
- Spot overextension: Use indicators like RSI or Stochastic to identify overbought or oversold conditions.
- Check levels: Look for prices straying far from a moving average or testing strong support/resistance zones.
- Enter: Wait for confirmation—enter only when the price shows signs of stalling or reversing near these extremes.
- Exit: Target a return to the average, such as the 20- or 50-period moving average, or the midpoint of the range.
Risk Management
- Place stop-loss orders beyond the extreme in case the price continues moving against you.
- Keep positions smaller than in trend-following trades since reversals may not always hold.
When to Avoid Mean Reversion
- During major news events, like central bank announcements or financial reports, when price swings can be extreme.
- In high-volatility environments where false signals are common.
Risk Management in Trading
Careful risk control remains essential whether trading with or against the trend.
1. Position sizing
Figure out how much you’re willing to risk on each trade before you start.
Formula:

Example: With a $10,000 account, if you risk 1% ($100) and your stop is 50 pips away, you are effectively risking $2 per pip. On EUR/USD, that translates to 0.2 lots. Proper position sizing ensures that no single trade can devastate your account.
2. Setting Your Stop-Loss
Just as you wouldn’t sail treacherous waters without a life jacket, you shouldn’t trade without a stop-loss. A stop-loss automatically exits your trade if the price reaches a predetermined level, protecting you from major losses if the market moves sharply against you.
Without a stop-loss, you risk constant stress, monitoring the market nonstop, and making impulsive decisions out of fear or fatigue. A well-placed stop-loss shields you from this emotional strain and helps you stick to your strategy.
How to Implement a Stop-Loss Strategy:
- Identify support and resistance levels using technical analysis. These act as natural benchmarks for placing your stop-loss.
- In volatile markets, give your stop-loss extra room to prevent it from being triggered by normal price fluctuations.
- Set a risk/reward ratio you are comfortable with. A 2:1 ratio is common because you only need to win 40% of your trades to be profitable. However, the ideal ratio depends on your market, strategy, and personal style.
- Consider using a trailing stop-loss to follow favorable price movements. Keep in mind, though, that in highly volatile conditions, trailing stops can be triggered prematurely.
3. Expectancy and Risk–Reward
Trading profitability is rooted in mathematics, not just intuition.
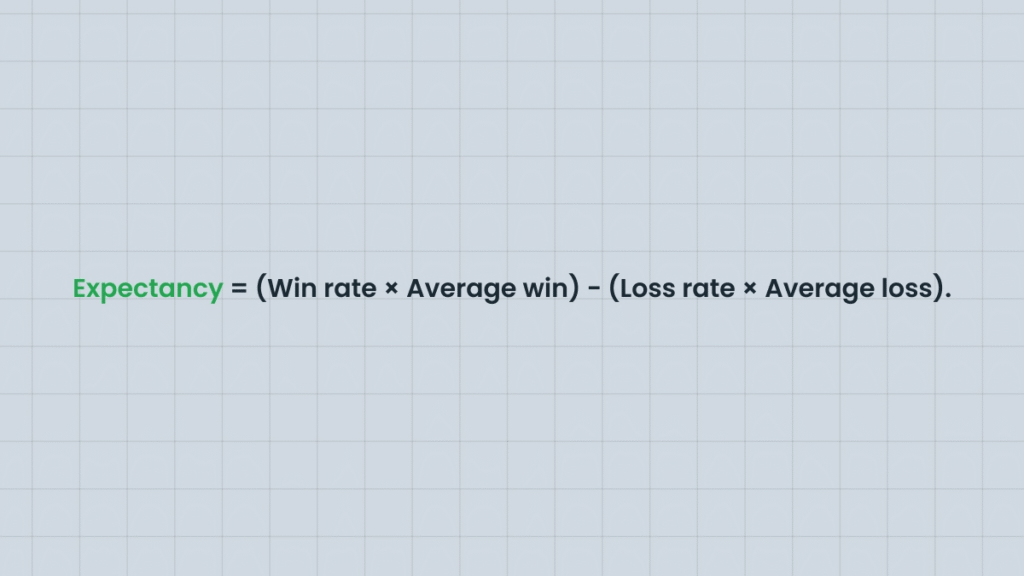
Example: Suppose you have a $10,000 account, risk 1% ($100), and set a stop 50 pips away. This means you are risking $2 per pip, or 0.2 lots on EUR/USD. Proper position sizing ensures no single trade can wipe out your account.
2. Setting Your Stop-Loss
Trading without a stop-loss is like sailing treacherous waters without a life jacket. A stop-loss automatically exits your trade when the price hits a predetermined level, protecting you from large losses in volatile markets.
Without a stop-loss, you risk constant stress, impulsive decisions, and emotional trading. Using one helps you stick to your plan and avoid burnout.
Implementing a Stop-Loss Strategy:
- Identify support and resistance levels using technical analysis as reference points for stop placement.
- In volatile markets, give your stop-loss extra room to avoid premature triggering by normal price swings.
- Decide on a risk/reward ratio that suits your style. A 2:1 ratio is common because it requires winning only 40% of trades to be profitable, but the optimal ratio depends on your strategy, market, and personal risk tolerance.
- Consider trailing stops to follow favorable price movements. Be aware that sudden volatility can trigger trailing stops prematurely.
3. Expectancy and Risk–Reward
Trading success is based on math, not intuition.
Example: If your win rate is 40%, with an average win of $200 and an average loss of $100, your expectancy calculation is: (0.4×200)−(0.6×100)=+20(0.4 \times 200) – (0.6 \times 100) = +20(0.4×200)−(0.6×100)=+20
This means you expect to earn $20 per trade on average. Even with more losses than wins, a positive expectancy keeps the strategy profitable over time.
4. Controlling Drawdowns
Managing risk also involves limiting losses beyond individual trades.
- Set daily or weekly loss caps. For example, if you lose 3% of your account in a day, stop trading.
- Track your equity curve. If your drawdown exceeds typical levels for your strategy, reduce position sizes until the account recovers.
Validating Your Strategy: Backtesting and Forward Testing
Before risking real money, test your strategy to ensure it works in different conditions. This reduces trial-and-error and helps you stick to your rules under pressure.
Backtesting:
Apply your strategy to historical data to see how it would have performed. Evaluate metrics like win rate, average win vs. loss, drawdowns, and expectancy. Weak results suggest the strategy may not work in live conditions.
Forward Testing:
Run your strategy in a demo account to test execution and timing in real-time conditions. Start small when moving to live trading to manage risk and confirm the reliability of your backtest.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced traders make mistakes that undermine strategy performance:
- Chasing both models simultaneously:
Trying to combine high win rate and high risk/reward often leads to inconsistency. Stick to the model that suits your personality. - Ignoring or moving stop-losses:
Moving or removing stops exposes you to large losses. Set logical stops and leave them, or use trailing stops to protect profits. - Oversizing positions:
Large positions can wipe out an account quickly. Stick to 1–2% risk per trade. - Trading counter-trend setups without structure:
Reversals require confirmation. Trading against the trend without a system is essentially gambling. - Neglecting expectancy math:
A high win rate alone does not guarantee profitability. Consider average wins and losses to ensure positive expectancy. - Lacking drawdown discipline:
Accept losing streaks and adjust risk accordingly. Don’t try to recover losses with oversized trades. - Ignoring market regimes:
Strategies perform differently in trending vs. ranging markets. Match your approach to the market condition, or sit out if conditions are unfavorable.
Glossary
- Trend: Sustained price movement in one direction.
- Mean reversion: Prices often return to an average after moving too far.
- Expectancy: Average profit or loss per trade, combining win rate and average win/loss size.
- Position sizing: Determining trade size based on account size, risk percentage, and stop distance.
- Slippage: Difference between expected and executed trade price due to market speed or liquidity.
FAQ
Q: What is the 2% rule?
Risk no more than 2% of your account per trade to limit losses.
Q: What is the 1% rule?
Risk no more than 1% per trade for more conservative risk management.
Q: What is a trailing stop-loss?
An order that automatically adjusts with price movement, locking in profits while allowing for further gains.
Q: Can stop-losses guarantee no losses?
No, but they limit losses to a predetermined level. Slippage and gaps can affect execution.
Q: Main types of stops:
- Stop order: Converts to a market order at your stop price.
- Stop-limit: Becomes a limit order; may not fill in fast markets.
- Trailing stop: Follows price automatically to lock in gains.
- ATR-based stops: Set based on market volatility.
- Structure-based stops: Placed beyond swing highs/lows.
Q: Where to place stops?
Depends on your strategy. In an uptrend, place below the last swing low or use ATR for volatile markets. Short-term traders may use tighter stops near support/resistance.
Q: What are gaps and slippage?
- Gap: Price jumps over levels, often after news or weekends.
- Slippage: Trade executes at a different price due to fast movement.
Small positions or closing before sessions end can mitigate these risks.
Q: When to adjust stops?
Move stops to break even once the trade moves favorably. Use trailing stops to lock in profits but never move stops further to avoid a loss, as this increases risk.
Get high-accuracy trading signals delivered directly to your Telegram. Subscribe to specialized packages tailored for the world’s top markets:
Free Crypto Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free Forex Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free VIP Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices) Subscribe via Telegram
Free Trading Acoount Open With ORON LIMITED Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices)
Open Account
Not profitable? Don’t worry! Join our copy trading system where we provide lower risk returns. Benefits of Joining Us:
-Lesser Risk as lot size is minimal
-Higher returns (approx. 5% to 10% monthly)
-Easy Deposit and Withdrawal with USDT using crypto wallets
-Lesser Drawdown
-Instant Support
-Invest Now and get guaranteed returns with us. DM us for more info❤️
-Start Now
*Copy Trading is free but we charge some percentage of profit as fees.*
Full VIP signals performance report for September 22–26, 2025: