
What is Forex?
Forex, short for Foreign Exchange, is the largest global marketplace for trading currencies. Traders navigating this market can encounter massive profit potential—but also significant risk. The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, offers high leverage, and provides access to a vast range of currency pairs.
What Are Forex Trading Strategies?
A Forex trading strategy is a structured plan outlining how you’ll trade. It defines when to open and close trades, what signals to follow, and which timeframes to use.
Some traders aim for quick, intraday moves using one-minute charts and technical indicators, while others base decisions on daily trends or economic news. The goal of a strategy is to replace guesswork with a consistent, rule-based approach. Trading without a strategy is like sailing without a map—you’re navigating the market blindly.
How to Create a Forex Trading Strategy (Step-by-Step)
- Identify your trading style
Decide whether you want to:- Scalp (minutes)
- Day trade (intraday)
- Swing trade (days–weeks)
- Position trade (weeks–months)
Your style determines chart timeframes and trade frequency.
- Choose your currency pairs
Pick pairs that match your trading style, such as EUR/USD or GBP/USD. - Define entries and exits
Base your decisions on technical indicators, chart patterns, or price signals. Set clear profit targets and stop-loss levels. - Assess risk tolerance
Decide your position size and risk per trade (typically 1–2% of your account). - Allocate time
Choose a style that fits your schedule. Day trading requires constant monitoring, while swing or position trading demands less frequent attention. - Plan around trading sessions
Forex liquidity and volatility fluctuate with global sessions. For example, the London–New York overlap is highly active, while the Asian session is quieter.
By following these steps, you can create a personalized framework, reducing impulsive and random trading.
When to Trade and Which Pairs to Choose
Timing and pair selection can provide an edge in Forex trading.
Forex Trading Sessions
Markets operate at different hours worldwide. When two sessions overlap, trading activity increases, spreads narrow, and price movements strengthen. Conversely, during single-session trading, liquidity is lower, spreads widen, and even minor news can trigger sharp swings. Aim to trade when liquidity is strong to reduce slippage and improve trade quality.
Choosing Currency Pairs
While any pair can be traded at any time, the outcome depends on session activity. Matching session timing with pairs increases efficiency:
- Tokyo & Sydney (00:00 – 07:00 GMT): Active pairs include AUD/USD, AUD/JPY, NZD/USD.
- London & Tokyo (07:00 – 09:00 GMT): Focus on Yen and Euro pairs.
- London & New York (12:00 – 16:00 GMT): Most active, especially EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY.
Major pairs offer narrow spreads and high liquidity, while less common pairs can be more volatile but riskier.
Diversification: Avoid trading multiple pairs that move together (like EUR/USD and GBP/USD). Spread risk across different currencies.
Strategy Styles by Timeframe
- Scalping (minutes)
- Pros: Many small gains, no overnight risk.
- Cons: Stressful, high fees, constant attention needed.
- Day Trading (intraday)
- Pros: Positions open and close same day, avoids overnight gaps.
- Cons: Long screen time, sensitive to spreads and noise.
- Swing Trading (days–weeks)
- Pros: Fewer trades, more time for analysis, captures bigger moves.
- Cons: Exposed to gaps, requires patience.
- Position Trading (weeks–months)
- Pros: Follows long-term trends, less daily effort, less short-term noise.
- Cons: Requires more capital, wide stops, strong discipline.
The Four Pillars of Forex Trading Success
- Solid Strategy
Trading without a plan is a common reason for losses. A solid strategy involves:- Defining goals: Are you aiming for quick profits or long-term growth?
- Analyzing the market: Use technical and fundamental tools to understand conditions.
- Selecting indicators: MAs, RSI, MACD, etc., help identify entry and exit points.
- Testing and optimizing: Backtest against historical data to refine your approach.
2. Robust Risk Management
Simple Risk Management Framework
Position Sizing
Determine how much to risk on each trade with this formula: Risk per Trade=Account Size×%Risk\text{Risk per Trade} = \text{Account Size} \times \% \text{Risk}Risk per Trade=Account Size×%Risk
Example: On a $10,000 account with 1% risk, your maximum loss per trade is $100.
Stop-Loss Placement
Place stops beyond points where your trade idea becomes invalid. For a long position, this could be below a support level.
Example: If you buy EUR/USD at 1.0800 and support is at 1.0780, a stop could be set at 1.0775.
Risk/Reward Ratio
Aim for trades where the potential reward is at least twice the risk: Target÷Risk≥2\text{Target} \div \text{Risk} \geq 2Target÷Risk≥2
Example: If you risk 20 pips, target 40 pips or more. Even with a 40% win rate, maintaining a 1:2 risk/reward ratio can result in long-term profitability.
No matter how strong your strategy, not every trade will succeed. Effective risk management ensures you can recover from losses and continue trading.
Key Techniques:
- Stop-Loss Orders: A safety net to protect your capital.
- Position Sizing: Adjust trade size based on account balance and personal risk tolerance.
- Diversification: Spread your exposure across multiple trades and currency pairs.
3. Strict Trading Discipline
Even the best strategy fails without discipline. Emotional decision-making can destroy results.
- Follow Your Plan: Stick to your strategy—don’t let market noise or impulses derail you.
- Keep a Journal: Record every trade and review what works and what doesn’t. This practice accelerates improvement.
- Be Patient: Not every moment presents an opportunity. Long-term success requires emotional stability.
4. Continuous Learning
The Forex market is constantly evolving, influenced by global economics, geopolitics, and technology. Traders must commit to lifelong learning.
- Adapt to Market Changes: Regularly adjust your strategies to reflect new market conditions.
- Learn from Others: Engage in forums, webinars, and mentorship programs for fresh insights and techniques.
- Expand Your Knowledge: Study economic indicators, market trends, and advanced tools to continually sharpen your skills.
Popular Forex Trading Strategies
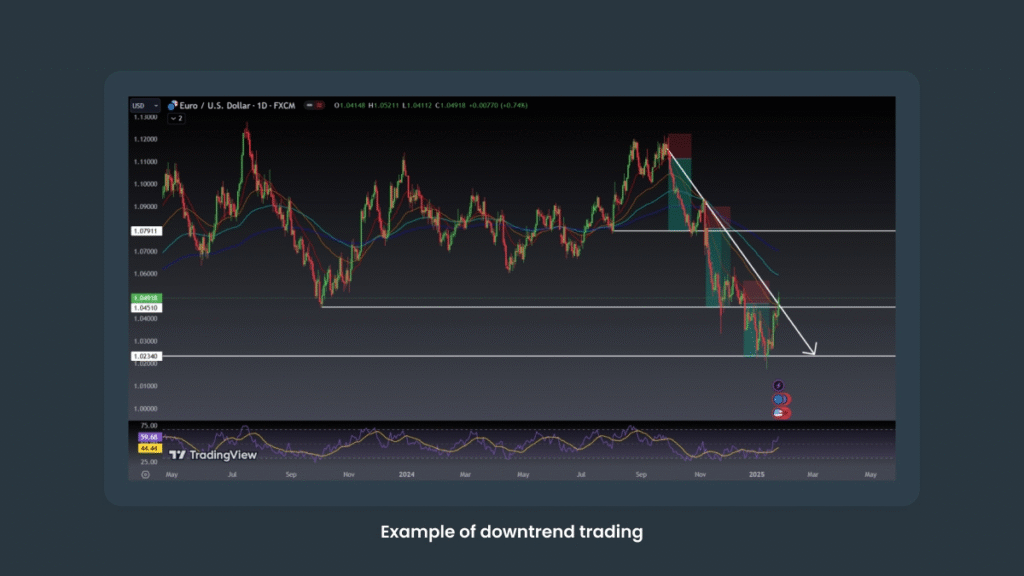
1. Trend-Following
“The trend is your friend.”
Trend-following is one of the most straightforward and widely used Forex strategies. It works best in markets that are clearly trending. Traders rely on technical indicators to identify the market’s direction, buying during uptrends and selling during downtrends.
Key Indicators:
- Moving Averages (SMA, EMA): Smooth out price data to confirm trends.
- Average Directional Index (ADX): Measures the strength of a trend.
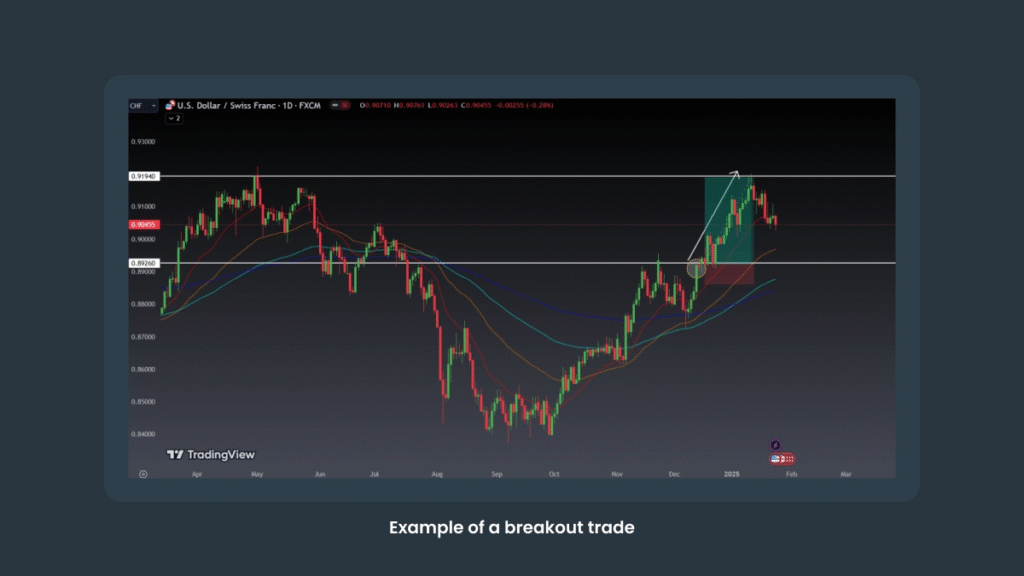
2. Breakout Strategy
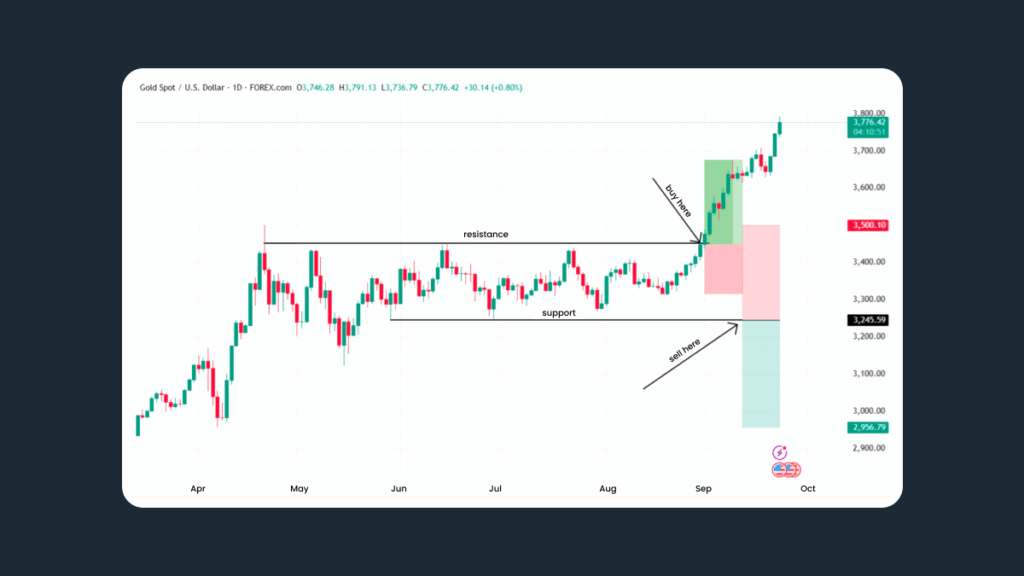
The breakout strategy works well in volatile markets. A breakout signals that price momentum is strengthening, and the asset may continue moving in the breakout direction for some time. When the price breaks above a resistance level, consider buying; if it breaks below a support level, consider selling.
To protect against false breakouts, place a stop-loss just outside the breakout zone.
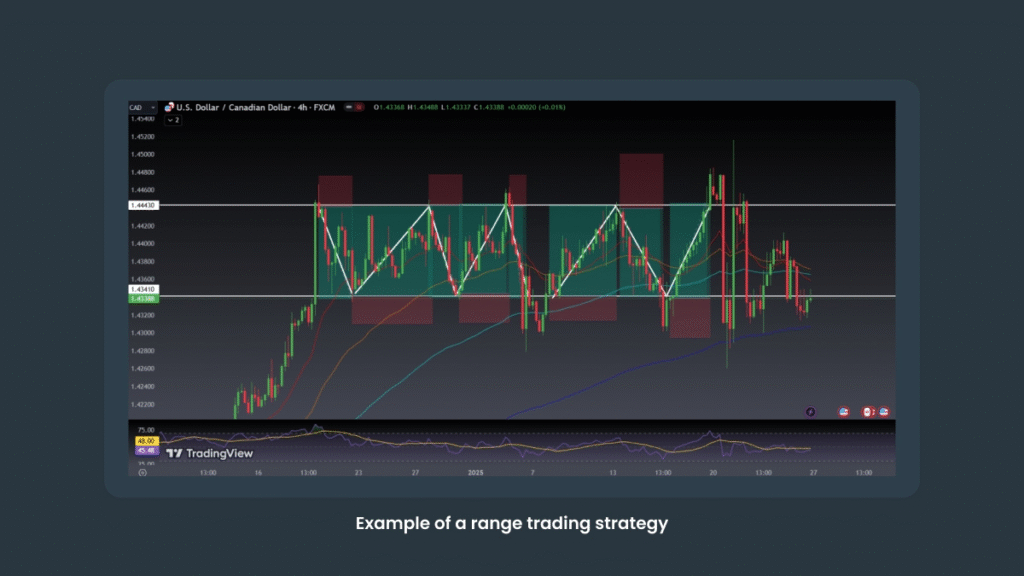
3. Range Trading
In markets with low volatility and no clear trend, opportunities come from prices oscillating within a defined range. The strategy involves buying near support levels and selling near resistance levels. Tools like the RSI or Stochastic Oscillator can help identify potential reversals by signaling overbought or oversold conditions.
Tip: Be aware of possible breakouts and always place a stop-loss to protect your position.
4. News Trading
Significant economic announcements and central bank decisions can trigger sudden, sharp market moves. Traders monitor these events and use the economic calendar to plan trades accordingly.
Risk: Around major reports, options and other instruments can become more expensive. Slippage and wider spreads are common, so using a stop-loss is essential.
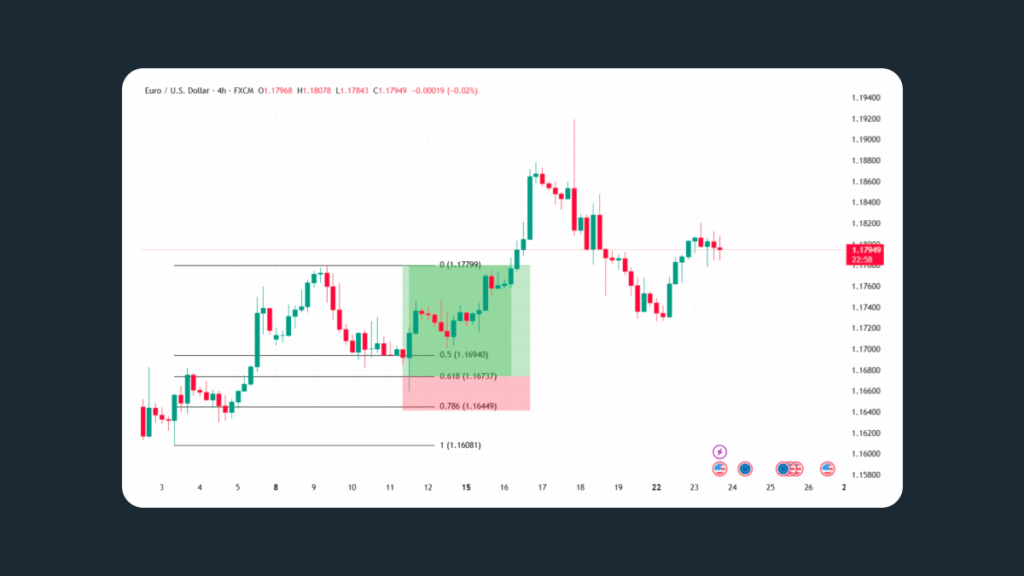
5. Retracement Trading (Fibonacci)
Markets rarely move in straight lines. Retracement trading focuses on pullbacks within an existing trend to identify potential re-entry points. Key Fibonacci levels—50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%—are often used to pinpoint areas where prices might reverse.
6. Carry Trade
This long-term strategy exploits interest rate differences between currencies. Traders borrow in a currency with a low interest rate and invest in one offering higher returns.
Example: Borrowing Japanese yen (JPY) at low rates and buying Australian dollars (AUD) to earn the interest rate differential.
Risk: Sudden changes in interest rates or unexpected “risk-off” events can erase profits quickly.
7. Grid Trading
Grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at fixed intervals around the current price, creating a “grid.” Profits are generated as the market oscillates between these levels.
Advantage: Allows profits in range-bound markets without needing to predict direction.
Risk: Can be dangerous in strong trends unless combined with stop-losses or equity protection.
Common Mistakes and Myths to Avoid
Even with a solid plan, mistakes can undermine your results. Here are frequent errors related to the strategies covered in this guide:
- Trading all hours of the day
Forex runs 24 hours, but that doesn’t mean you should trade nonstop. Beginners often waste energy during slow sessions with wide spreads and minimal movement. Focus on the sessions and pairs that fit your trading style. - Ignoring session overlaps
The London–New York overlap is the most active period, yet many traders miss it. Trading during less liquid hours can result in poor execution and fewer quality setups. Timing is as important as your strategy, so plan trades during high-liquidity sessions. - Skipping risk management
Always use appropriate position sizes and stop-losses to protect your capital. Risking more than 1–2% per trade can deplete your account quickly. - Lacking discipline and trading impulsively
Even the best strategy fails if rules aren’t followed. Stick to your plan, be prepared for losing trades, and wait for quality opportunities. Chasing moves or acting on impulse will undo your strategy’s effectiveness.
FAQs
1. What’s the best strategy?
There is no single “best strategy.” Beginners should start slowly—follow trends or trade breakouts—and practice on a demo account to build experience. Adjust your approach as you learn what fits your style, capital, and schedule.
2. How much money is needed to start?
You don’t need a large account. Start with a few hundred dollars if you manage risk carefully, keeping each trade small and limiting risk to 1–2% of your balance.
3. Is Forex trading risky?
Yes, markets are unpredictable. You can reduce risk by using indicators, confirming setups, monitoring active sessions, and setting stop-losses and profit targets. Leverage amplifies both potential profits and losses.
4. How much time does trading require?
It depends on your style. Scalping and day trading need constant monitoring and quick decisions. Swing or position trading requires less screen time, allowing trades to develop over days or weeks.
Glossary
Indicators: Tools to analyze price data and identify trends, momentum, volatility, or potential reversals (e.g., RSI, MACD).
Pip: The smallest price movement in most currency pairs, usually the fourth decimal place. For example, EUR/USD moving from 1.0800 to 1.0805 equals 5 pips.
Spread: The difference between the bid and ask price; it represents the cost of entering a trade. Smaller spreads mean cheaper trades.
Leverage: Allows you to control more capital than your deposit. Example: 1:50 leverage lets you trade $50,000 with $1,000. It can magnify profits, but also increases potential losses.
Drawdown: Measures the percentage decline of an account after losses. Example: dropping from $10,000 to $9,000 is a 10% drawdown. Keeping drawdowns small helps sustain your account.
Moving Average (MA): Averages price over a set number of periods (e.g., 20 or 50) to smooth out trends.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Momentum indicator scaled 0–100. Above 70 indicates overbought; below 30 indicates oversold.
MACD: Compares two moving averages to identify trend changes and momentum shifts.
Stochastic Oscillator: Compares the closing price to a recent range; above 80 signals overbought, below 20 signals oversold.
ADX (Average Directional Index): Measures trend strength. Above 25 indicates a strong trend; below 25 signals a weak or sideways market.
Fibonacci Retracements: Highlight potential pullback levels in trends, such as 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%, typically shown as horizontal lines between a high and a low.
Get high-accuracy trading signals delivered directly to your Telegram. Subscribe to specialized packages tailored for the world’s top markets:
Free Crypto Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free Forex Signals Subscribe via Telegram
Free VIP Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices) Subscribe via Telegram
Free Trading Acoount Open With ORON LIMITED Signals (Gold, Oil, Forex, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Indices)
Open Account
Not profitable? Don’t worry! Join our copy trading system where we provide lower risk returns. Benefits of Joining Us:
-Lesser Risk as lot size is minimal
-Higher returns (approx. 5% to 10% monthly)
-Easy Deposit and Withdrawal with USDT using crypto wallets
-Lesser Drawdown
-Instant Support
-Invest Now and get guaranteed returns with us. DM us for more info❤️
-Start Now
*Copy Trading is free but we charge some percentage of profit as fees.*
Full VIP signals performance report for September 22–26, 2025:
